Shipping to Australia can be complex due to its distance from major markets and strict import regulations. This guide simplifies the process by covering Australia’s trade overview, major gateways, customs rules, freight choices, and what businesses should know about shipping from China to Australia.
Australia’s Global Trade Overview
Australia plays a significant role in international trade, with its economy heavily supported by both exports and imports. In 2024, the country recorded total exports of US$340.85 billion and total imports of US$296.48 billion, resulting in a trade surplus of US$44.37 billion. Australia’s trade relationships are strongly anchored in the Asia Pacific region and the United States.
Export
The largest destinations in 2024 were China, Japan, and South Korea. Key export commodities included mineral fuels and oils, ores and slag, and precious stones and metals, underscoring Australia’s role as a global supplier of raw materials and energy.
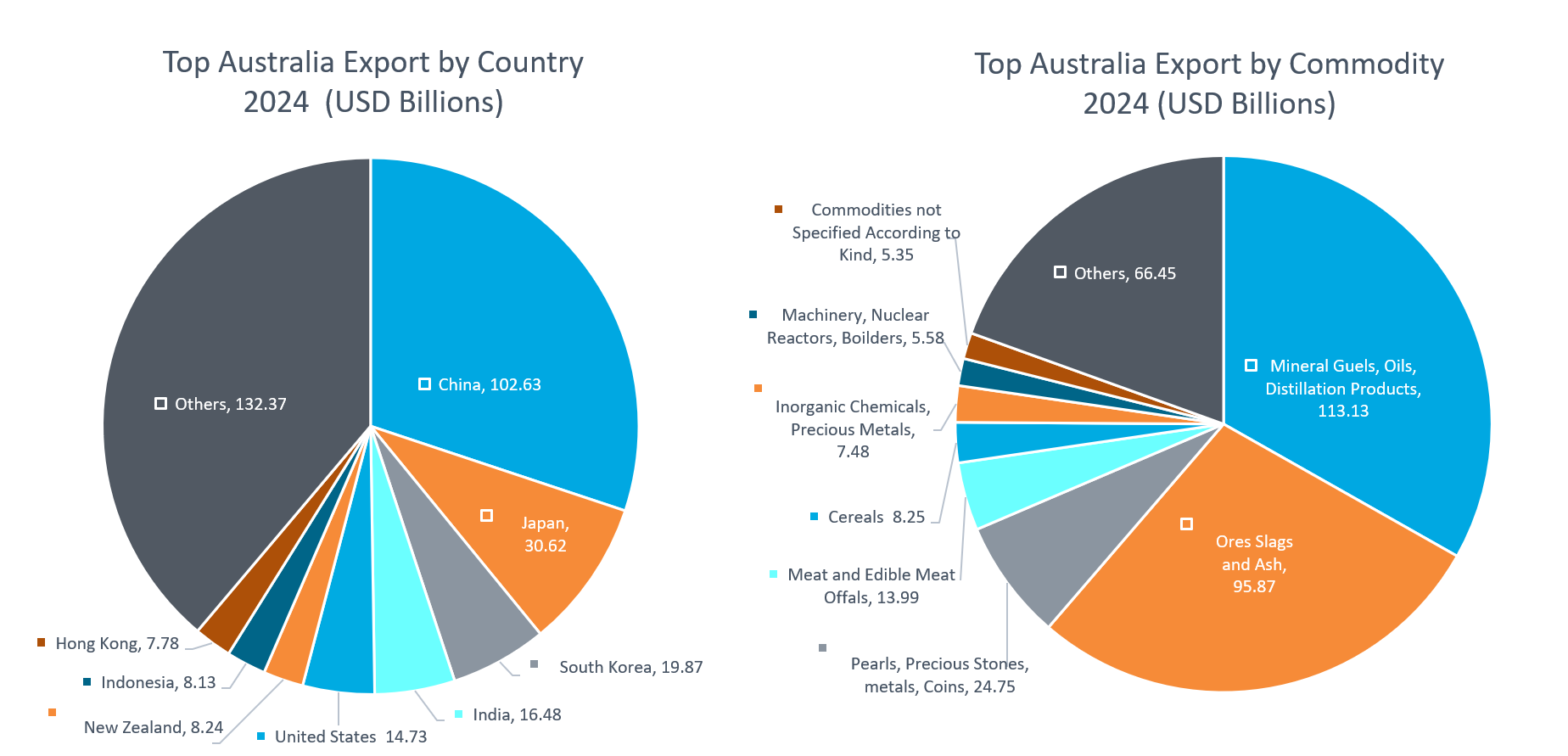
Import
Australia’s top sources were China, the United States, and Japan. Leading imports included vehicles, machinery and nuclear reactors, and mineral fuels and oils, reflecting the country’s reliance on advanced technology, transport equipment, and energy products.
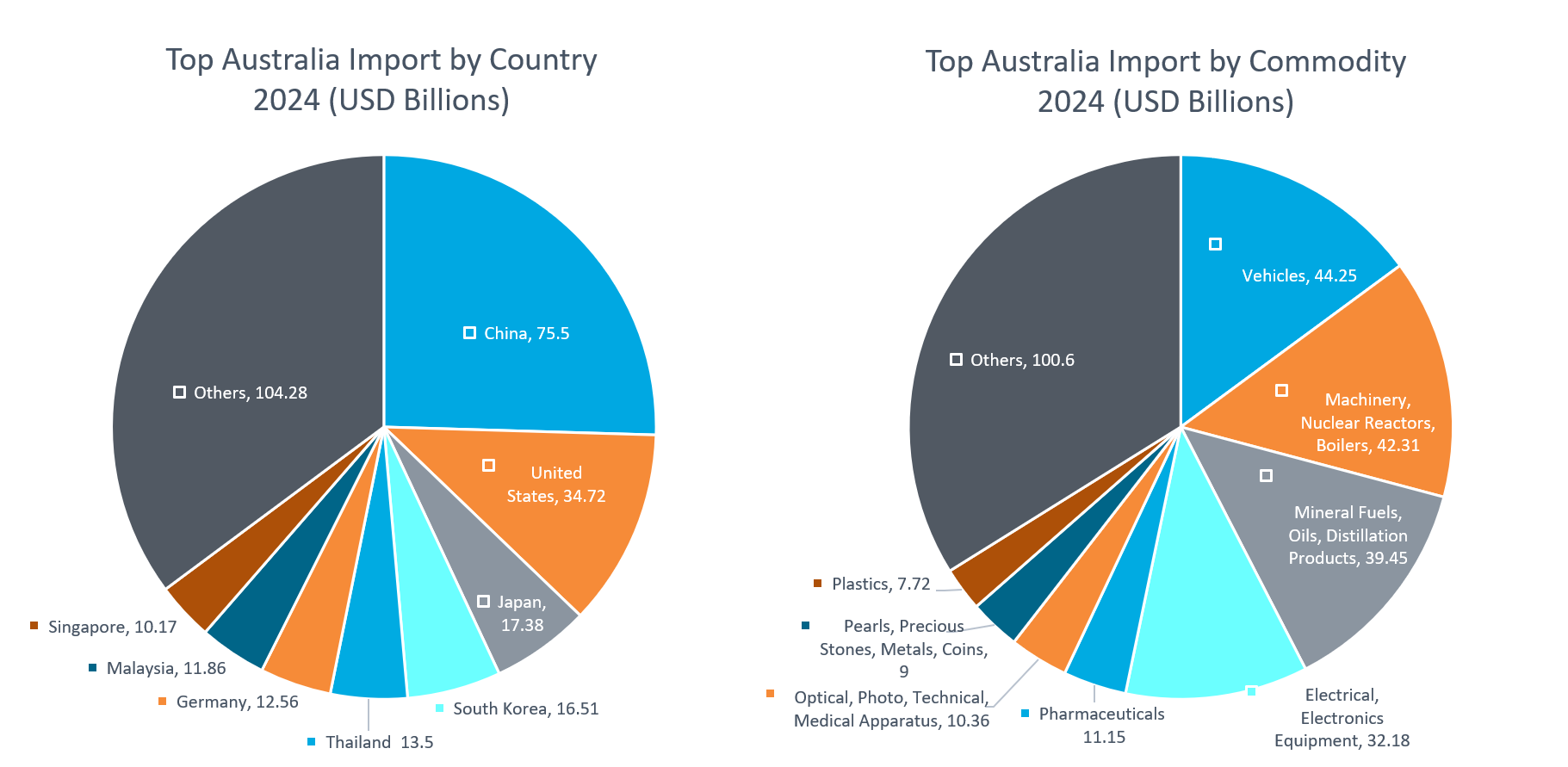
Australia also benefits from an extensive network of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) that reduce tariffs and strengthen supply chains. Some of the most important agreements include ChAFTA, AUSFTA, KAFTA, JAEPA, CPTPP, RCEP, A UKFTA, and AI ECTA.
Major Gateways in Australia
Australia’s imports and exports depend on efficient gateways that connect it to global markets. Seaports handle most trade by weight, moving bulk commodities, raw materials, and containerized cargo vital for mining, agriculture, and manufacturing. Airports, by contrast, manage high value and time sensitive goods such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and perishables, where speed and reliability outweigh volume. Together, they ensure Australia’s trade flows remain competitive and resilient.
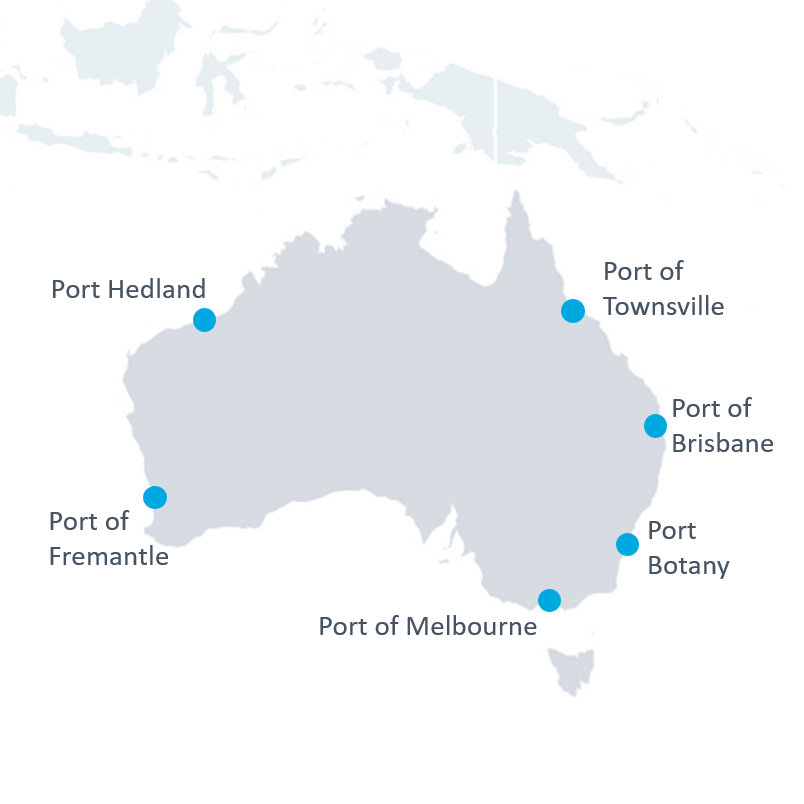
Seaports
| Seaports | Feature |
|---|---|
| Port of Melbourne | Australia’s largest container port, handling about 3 million TEUs annually, with extensive rail and inland connections. |
| Port Botany (Sydney) | A major hub for New South Wales, processing a large share of Sydney’s container traffic and petroleum imports. |
| Port of Brisbane | A multi cargo hub supporting Queensland’s agricultural and mining exports. |
| Port of Fremantle | Western Australia’s main port for container and bulk cargo. |
| Port Hedland | The world’s largest bulk export port, specializing in iron ore. |
| Port Townsville | North Queensland’s key gateway for minerals, sugar, and vehicles. |
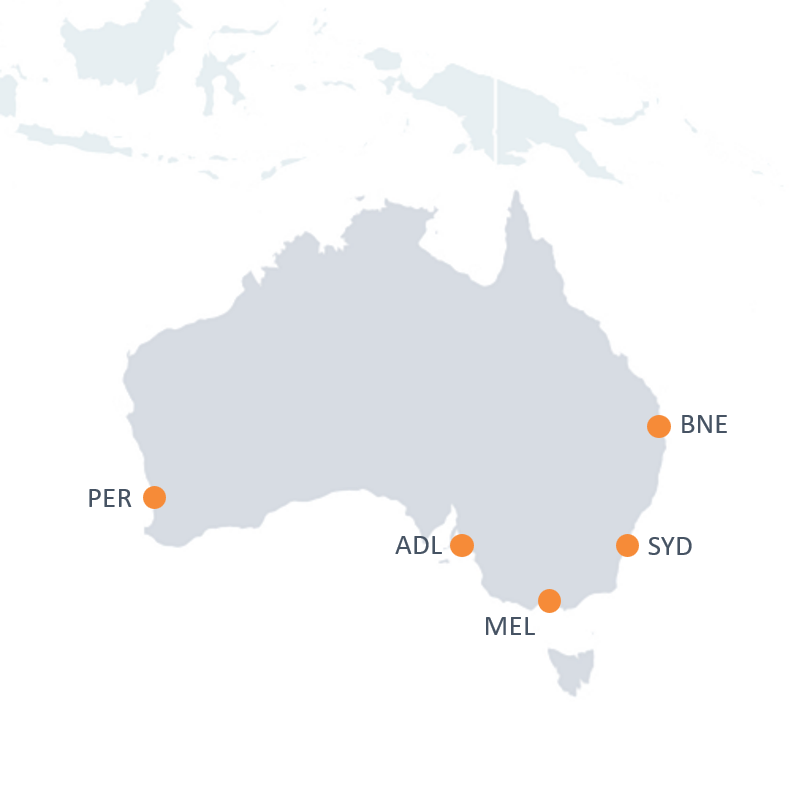
Airports
| Airports | Feature |
|---|---|
| Sydney Airport (SYD) | Australia’s busiest airport, handling a significant share of air cargo along with the highest passenger volumes |
| Melbourne Airport (MEL) | A leading air freight hub, operating 24 hours with dedicated freighter aprons and strong infrastructure for both imports and exports |
| Brisbane Airport (BNE) Perth Airport (PER) Adelaide Airport (ADL) |
Important cargo and passenger gateways that enhance connectivity for regional industries and international markets |
Customs Rules for Shipping to Australia
For companies shipping to Australia, customs compliance is critical. Australia’s border rules extend beyond duties and tariffs, with biosecurity and documentation as top priorities.
- Biosecurity and Quarantine: Goods like timber, seeds, food, and animal-based materials often require permits, inspections, or treatments. Wooden pallets must comply with ISPM 15 standards.
- Import Declarations: Shipments valued above AUD 1,000 require a formal declaration through the Integrated Cargo System (ICS). Importers often work with licensed brokers, while exporters should provide accurate invoices and certificates of origin.
- Duties and GST: Most imports are subject to a 10% GST, applied on the customs value, freight, and duties. Importers may benefit from Tariff Concession Orders (TCOs) and FTAs if certificates of origin are provided.
A global provider of advanced drilling technology engaged Dimerco Australia to handle shipments from China to Australia under the China–Australia Free Trade Agreement (ChAFTA). Australia’s customs requirements are highly complex, posing challenges for securing preferential duty treatment. Leveraging years of hands-on experience, Dimerco Australia ensured accurate HS code classification and provided expert duty and tax management. As a result, the customer achieved 100% duty savings while maintaining full compliance.
Choosing the Right Shipping Mode: Air vs. Ocean
When shipping to Australia, the choice between air and ocean freight depends on cost, urgency, and commodity type.
Air Freight
The fastest mode, suitable for high value and low volume goods such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, or perishables. Delivery takes 1 to 7 days, depending on the route, but costs are higher. Although air freight can cost up to 10 times more than ocean freight, there are strategies to help lower your international air freight costs. Learn how to reduce international air freight costs here.
Ocean Freight
For less urgent and lower-value cargo, ocean freight is the better option. Shipping to Australia via ocean freight will take between 2 to 6 weeks depending on the route and the service. Ocean shipping is far more economical and allows up to 67 CBM of cargo in a 40-foot container. Although ocean shipping already offers lower rates, there are still ways to further optimize your shipping costs. Discover how to reduce your container shipping costs here.
| Factor | Air Freight | Ocean Freight |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Premium | Economical |
| Transit | Fast (1 to 7 days) | Slow (2 to 6 weeks) |
| Best For | Urgent, perishable, high value goods | Bulk, heavy machinery, raw materials |
Shipping from China to Australia
With trade tensions between the United States and China, many exporters are diverting shipments to Australia, one of China’s closest and most important partners. This has increased the volumes of companies shipping from China to Australia, creating new opportunities but also requiring careful logistics planning.
- Trade Overview: China is Australia’s largest partner, with key exports including machinery, electronics, textiles, and consumer goods.
- Ocean Freight: Major routes connect Shanghai, Ningbo, and Shenzhen to Melbourne, Sydney, and Brisbane. Transit times are typically 12 to 22 days.
- Air Freight: A faster option with 1 to 5 days of transit times and direct flights between major cities. Costs are higher but ideal for electronics, e commerce, and urgent shipments.
- Customs Considerations: Importers should prepare accurate documentation and certificates of origin to claim tariff benefits under the China Australia Free Trade Agreement (ChAFTA).
Ready to Start Shipping to Australia?
The rising demand for shipping from China to Australia highlights how trade flows are shifting in response to global tensions. Companies that plan ahead, understand customs requirements, and choose the right mode of transport will gain a competitive advantage. By aligning with experienced logistics partner, like Dimerco Australia, and leveraging trade agreements like ChAFTA, businesses can reduce costs and ensure supply chain resilience in this evolving market. Looking to ship to Australia? Start a discussion with us today to simplify your global trade.
