At the heart of international trade, the container shipping industry plays a pivotal role, facilitating the seamless movement of goods and driving economic growth and globalization.
However, this sector has encountered a host of challenges in recent years, ranging from geopolitical conflicts and inflation to oversupply and container surges. Amidst these complexities, the industry faces a growing concern—the escalating environmental impact, requiring immediate and transformative action. As ocean shipments remain a popular choice for their efficiency and lower fuel consumption, it’s imperative to address the reality that they contribute significantly to energy-related emissions.
Exploring options such as LNG dual-fuel and methanol dual-fuel vessels emerges as a promising solution to steer container shipping toward a sustainable future. This blog highlights the advantages of these fuels in terms of sustainability and environmental compliance, shedding light on their potential to transform the shipping industry’s ecological impact.
The environmental challenges of traditional shipping fuels
The environmental impact of traditional marine fuels is severe, presenting a considerable challenge to global environmental sustainability. Here are some key details that shed light on the gravity of the situation:
- The shipping sector heavily relies on fossil fuels, making it one of the largest consumers of petroleum-based products.
- Approximately 95% of ships today are powered by internal-combustion engines (ICEs) running on various petroleum products, including heavy fuel oil (HFO), marine gas oil (MGO), and marine diesel oil (MDO).
- Among these fuels, heavy fuel oil, commonly known as bunker oil, exhibits a tar-like consistency, leading to devastating consequences like oil spills that harm delicate ecosystems, as witnessed in recent incidents such as the 2020 Mauritius oil spill disaster.
These ships, propelled by fossil fuels, not only discharge oil, fuel, and waste into the water but also emit exhaust fumes into the atmosphere, resulting in multiple environmental issues, such as air pollution and interference with biodiversity, leading to the endangerment and extinction of various species. For instance, the burning of heavy fuel oil releases harmful pollutants and greenhouse gasses, contributing to climate change and posing health risks to both marine life and coastal communities.
The scale of marine fuel consumption is immense, with the annual global marine fuel consumption projected to reach around 330 million metric tons (87 billion gallons) annually, surpassing the world’s yearly jet fuel consumption of 220 metric million tons (58.1 billion gallons). Furthermore, the overall demand for marine fuels is expected to double by 2030 due to the surge in global trade. (Source: US Department of Transportation Maritime Administration)
Given the substantial environmental challenges posed by traditional shipping fuels, finding sustainable and greener fuel solutions becomes vital for the shipping industry. The exploration and adoption of alternative fuels, such as LNG dual-fuel and methanol dual-fuel vessels, emerge as promising measures to mitigate the detrimental impact on our oceans and atmosphere, ushering in a more sustainable future for container shipping.
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) commitment to greener shipping
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has implemented new regulations aimed at curbing greenhouse gas emissions in the global ocean shipping industry. To achieve this goal, the IMO utilizes energy-efficient indicators like the Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI) and Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII), mandating shipping companies to reassess their vessels, invest in fleet upgrades, and adopt new fuel technologies to foster greener practices in the industry.
This commitment to green shipping reflects the IMO’s dedication to combating climate change within the maritime sector. Furthermore, in 2018, the IMO approved a comprehensive greenhouse gas strategy, setting ambitious targets of reducing carbon emissions by 40% by the end of 2030 and an even more significant 70% by the end of 2050. These initiatives chart a course towards sustainability and highlight the urgent need for exploring alternate fuels for ocean shipping to achieve greener practices.
Understanding alternate fuels for ocean shipping
As the industry progresses towards net-zero emissions, alternate fuels are emerging as future trends in the new shipbuilding market. These alternative fuels include LNG, methanol, biofuel, and e-fuels, which are increasingly considered to meet emission targets.
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) emerges as a top-leading option in the quest for greener shipping practices, garnering endorsement from the IMO for its zero sulfur content and environmentally favorable attributes. The production process of LNG involves the purification and supercooling of natural gas to a liquid state at temperatures reaching approximately -260° fahrenheit, facilitating its storage and transportation. During the liquefaction process, extraneous compounds are removed, leaving primarily methane with minimal amounts of other hydrocarbons, creating a cleaner and more sustainable fuel source.
The key benefits of using LNG include:
- Low Sulfur Content: Reduces the environmental impact and contributes to improved air quality in marine environments.
- Reduced Particulate Matter: Contributes to enhanced air quality and mitigating health risks for marine life and coastal communities.
- Lower Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) Emissions: LNG combustion supports efforts to combat nitrogen oxide pollution and its harmful effects on the atmosphere.
- Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Contributes to the overall effort to combat climate change and meet emission reduction targets when compared to conventional fossil fuels.
- Abundant Availability: With vast reserves of natural gas, LNG ensures a stable and secure supply chain for the shipping industry.
- Easier Compliance with Emission Regulations: This positions LNG as a preferred option for shipowners and operators seeking to meet evolving environmental standards.
- Noise Reduction: Contributes to reduced underwater noise pollution and its potential impact on marine ecosystems.
The adoption of LNG as an alternate for ocean shipping offers significant potential for reducing the shipping industry’s environmental footprint and aligning with international efforts to achieve sustainable and eco-friendly container shipping practices. (source: Alternative Fuels Data Center)
Methanol
Methanol stands out as a highly promising alternative fuel in the pursuit of green shipping practices, offering a range of compelling advantages that position it as a frontrunner in the transition towards sustainable container shipping. The key benefits of Methanol as a green shipping fuel include:
- Simplified Storage and Handling: Its liquid form enhances operational efficiency and reduces logistical challenges for shipping companies.
- Lower Particulate Matter (PM) and Black Carbon Emissions: Methanol’s cleaner combustion process contributes to improved air quality and reduced health risks for both marine life and coastal communities.
- Extended endurance for longer voyages: With a higher energy content per volume than ammonia or hydrogen, making it suitable for a variety of vessels and longer voyages, requiring less frequent refueling.
- Wide availability: This eco-friendly fuel can be produced from various feedstocks, offering shipping companies flexibility in sourcing and supply chain management.
- Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure: Methanol’s ease of storage and handling reduces the need for extensive modifications or retrofitting.
- Safety: It is less flammable than some other fuels, enhancing safety during storage and handling procedures on board vessels.
These advantages showcase Methanol’s practicality and versatility as an alternative fuel for shipping, making it an attractive option for the industry’s transition towards greener and more sustainable practices.
By exploring and adopting these alternate fuels, the shipping industry can align with the IMO’s ambitious emission reduction targets and pave the way towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future for container shipping.
Biofuels
Biofuels are renewable fuels derived from organic materials such as plant oils, animal fats, and agricultural waste. They hold great potential in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and advancing circular economy principles by utilizing waste materials as valuable feedstock for fuel production. Biofuels offer several noteworthy advantages in the context of green shipping practices:
- Low Sulfur and Nitrogen Content: Contributes to cleaner combustion and reduced emissions of harmful pollutants like sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). This characteristic aligns with environmental regulations aimed at enhancing local air quality and reducing the shipping industry’s environmental impact.
- Low Carbon Intensity: With fewer carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions released compared to Conventional fossil fuels, their adoption contributes to meeting emission reduction targets and combating climate change in the shipping sector.
- Circular Economy Benefits: Utilizes organic waste materials as feedstock for biofuel production, turning waste into valuable resources and reducing the reliance on finite fossil fuel reserves.
- Potential for Carbon Neutrality: Advanced biofuels, derived from algae or certain feedstocks, have the potential to achieve this or even become carbon-negative, making a significant contribution to the shipping industry’s sustainability goals.
Despite the promising advantages, it’s important to acknowledge that the shipping sector is still in its early stages of exploring and adopting biofuels. The successful integration of biofuels into mainstream shipping operations requires continued research, infrastructure development, and collaboration between stakeholders to ensure their availability and practicality on a global scale.
As the maritime industry seeks to transition towards greener practices, biofuels represent a promising avenue to reduce carbon intensity, improve local air quality, and advance sustainability efforts, aligning with the shipping industry’s commitment to a more environmentally responsible future.
The emergence of LNG Dual-Fuel Vessels in container shipping
In recent years, the emergence of LNG dual-fuel technology has marked a significant shift in the container shipping industry towards greener and more sustainable practices. LNG dual-fuel vessels are equipped with engines that can run on both traditional marine fuels and liquefied natural gas (LNG). This innovative technology offers numerous advantages, making it an attractive option for shipping companies seeking to:
- Reduce their environmental impact and comply with strict emission regulations.
- Significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, including carbon dioxide (CO₂).
- Lower sulfur oxide (SOx) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, leading to improved air quality in marine environments.
To showcase the viability of this technology, several shipping companies have adopted LNG dual-fuel vessels, successfully integrating them into their fleets. However, transitioning to LNG dual-fuel vessels also presents challenges and considerations, including:
- The need for infrastructure development to support LNG bunkering and storage facilities.
- Ensuring a stable LNG supply chain and availability in various ports.
- Managing the initial investment costs associated with retrofitting or building new LNG dual-fuel vessels.
However, with the demonstrated environmental benefits and increasing industry support, LNG dual-fuel vessels are positioned to play a transformative role in shaping the future of container shipping and driving the industry towards a more sustainable and eco-friendly direction.
The potential of methanol dual-fuel vessels in container shipping
These vessels boast engines capable of running on conventional marine fuels as well as methanol, providing a cleaner and more sustainable solution. Shipping giants such as Evergreen and CMA CGM have started ordering methanol dual-fuel vessels and developing future supply and infrastructure for methanol.
According to Alphaliner Weekly Newsletter, in the global new shipbuilding orders from January to February 2023, an impressive 62% of orders are for methanol dual-fuel vessels, showcasing the industry’s strong commitment to adopting this technology. Methanol dual-fuel vessels offer significant environmental benefits, such as reduced CO2 emissions and lower particulate matter emissions, contributing to combating climate change and improving air quality. However, transitioning to this technology requires addressing challenges like infrastructure development for methanol bunkering, ensuring fuel availability, and complying with evolving regulations.
Despite these challenges, the environmental advantages and long-term sustainability potential make methanol dual-fuel vessels a compelling choice for steering the container shipping industry towards a greener and more eco-friendly future.
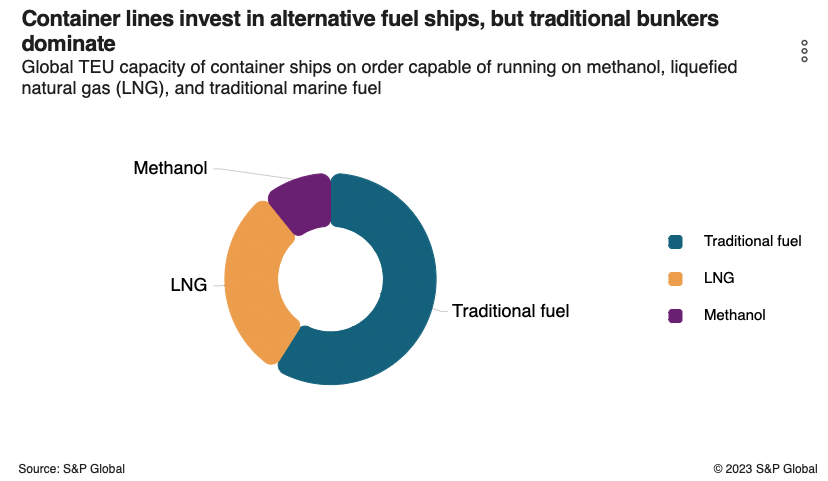
Comparing fuel choices
A comparison of fuel adoption in the industry reveals an undeniable sense of urgency to transition away from diesel and natural gas. Although some container ships have begun investing in alternative fuel vessels, traditional marine fuel remains heavily utilized.
Currently, a significant portion of containerships still heavily relies on traditional bunkers, indicating that further efforts are needed to accelerate the adoption of cleaner and more sustainable fuels like methanol and LNG. As the industry continues to navigate the path towards greener shipping practices, addressing challenges and promoting awareness of the benefits of alternate fuels will be crucial in achieving a more eco-friendly container shipping sector.
Fueling a more sustainable future
The rise of alternate fuels for ocean shipping presents a key opportunity for the industry. By embracing greener fuels like LNG and methanol dual-fuel vessels, shipping can play a crucial role in sustainability and combating climate change. As global trade demands increase, prioritizing eco-friendly practices to minimize the environmental footprint becomes essential. Ongoing research and technological advancements offer promising prospects for even cleaner and more sustainable fuel options.
Aligning with evolving regulations and addressing concerns related to these fuels can pave the path towards a greener and more environmentally friendly container shipping sector. Emphasizing sustainability as a guiding principle will shape the industry’s future, ensuring economic growth aligns with environmental stewardship. If you want to reduce logistics-related emissions and energy use let’s start a conversation and explore greener freight options for your supply chain. Together, we can revolutionize your supply chain and make a positive impact on the environment.