Semiconductors are the backbone of our interconnected digital world. These electronic chips power the devices we rely on daily, from smartphones and satellites to the electric cars revolutionizing transportation. Despite their size, semiconductors have immense influence, ranking as the world’s 4th most traded commodity and playing a crucial role in the advancement of modern electronics.
In a landscape where a few select countries dominate the semiconductor supply chain, Taiwan is the primary hub for manufacturing these components. This article examines Taiwan’s strategic expertise within the semiconductor supply chain and explores the intricacies of its logistics, highlighting the important role it plays in shaping the landscape of semiconductor manufacturing.
Taiwan’s Dominance in Semiconductor Manufacturing
Taiwan stands as the epicenter of global semiconductor manufacturing, producing over 60% of the world’s semiconductors. The country hosts numerous semiconductor facilities, which collectively contributes to a substantial 15% of its GDP. These facilities are equipped with top-tier capabilities for various stages of semiconductor production, including processes, assembly, packaging, and testing.
![]()
Taiwan’s journey in the semiconductor industry started in 1974 and has maintained its dominance since, continuously adapting to evolving market dynamics, technological advancements and global challenges. A key figure in this success story is the Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), the world’s largest chip manufacturer and the first company exclusively offering semiconductor foundry services, a pioneering move that established Taiwan as a leader in this field.
Semiconductors, known for their intricate and complex manufacturing processes, rely on the precise movement of valuable materials and components from companies worldwide. Taiwan excels in managing shipping and logistics with exceptional competence.
As leaders in this field, Taiwan’s semiconductor companies are crucial to the global supply chain. In 2022, they produced 60% of the world’s semiconductor chips, generating $40.2 billion out of the $57.4 billion made worldwide. Any disruptions in this supply chain would not only affect Taiwan but also cause a ripple effect for businesses worldwide, emphasizing Taiwan’s position in the global semiconductor landscape. Disruptions in the supply chain would have repercussions for not only Taiwan but to businesses all over the world.
Taiwan’s Role as a Semiconductor Innovation Hub
Beyond its manufacturing strength, Taiwan is also a strategic hub for semiconductor research and development (R&D). Taiwanese universities and research institutions collaborate closely with industry leaders to foster innovation and drive technological advancements. This strong R&D ecosystem enables Taiwan to stay at the forefront of semiconductor technology, continually developing new processes, materials, and designs that enhance the performance and efficiency of semiconductor devices.
Challenges in semiconductor manufacturing
While Taiwan is a powerhouse in semiconductor manufacturing, it faces challenges that affect its position in the industry:
The global chip shortage
The chip shortage of 2020 severely impacted the semiconductor supply chain. A surge in demand for chips exceeded supply capacity, leading to repercussions. Automakers experienced production halts, causing significant disruptions in the automotive industry. Electronic product launches were delayed, and consumers felt the impact through price inflation. This crisis emphasizes the critical role of chips in various sectors and how this would negatively affect the global economy.
Global geopolitical tensions
The concentration of supply chain capabilities in Asia, particularly in Taiwan, South Korea, and China has led to concerns about supply chain vulnerabilities. This focus exposes the supply chain prone to trade disputes and geopolitical tensions.
Taiwan’s strength in microchip production, referred to as its “Silicon Shield”, became evident as military tensions with China threatened chip supply chains. China’s investments in government led chip development programs have raised international eyebrows, especially given the escalating tensions with Taiwan. Recognizing the risks associated with overreliance on outsourcing, the US took proactive measures. President Joe Biden signed the CHIPS and Science Act, allocating $280 billion in domestic research on semiconductor manufacturing in the US.
Talent shortages
With more countries committing investments for domestic chip production and companies racing to construct new manufacturing facilities, the global demand for semiconductor talent has surged. Deloitte’s 2023 semiconductor industry outlook states that this translates to a need for more than 100,000 additional semiconductor workers each year.
While this talent shortage could potentially pose challenges, Taiwan has taken proactive measures to address this issue. Both the government and businesses are actively funding university programs to ensure a consistent supply of skilled talent to support the semiconductor industry’s growth.
Navigating the complex supply chain and logistics
In the past, semiconductor companies used to handle everything from designing their products and manufacturing equipment to performing both frontend and backend operations on a single site. However, as devices became more complex and demand increased, companies began relocating their operations to regions with lower labor cost such as Asia.
Today, the semiconductor industry operates on a global scale, involving various production stages like design, manufacturing, testing, packaging, and distribution. This global ecosystem relies on different regions for specialized functions.
![]()
Design: This initial phase defines the chip’s function, size, cost, and power consumption. It’s primarily led by US companies such as Intel Corporation, NVIDIA, Qualcomm and Micron Technology, whose strength is in research and development (R&D).
Manufacturing (Fabrication): The chip’s physical creation occurs in manufacturing facilities known as “foundries” or “fabs.” These fabs are key to the production process, with many located in Taiwan, China, and South Korea.
Testing: Once manufactured, chips undergo rigorous testing to ensure proper functionality. Subsequently, they are assembled into products ready for integration into various devices.
Distribution: Finished products are shipped globally to businesses, retailers, and consumers. Managing this stage involves critical logistics functions:
- Packaging Services: Preventing damage during transit is crucial, so packaging is meticulously handled.
- Merge in Transit: Combining shipments from multiple locations streamlines logistics.
- Air Export of Wafers: This facilitates efficient transport of delicate components.
- Service Parts Logistics: Ensuring the availability of essential manufacturing equipment parts.
The semiconductor chip journey
To create a semiconductor chip, the journey can span up to 100 days, requiring components to cross international borders 70 times. This journey starts with the creation of silicon wafers and their transformation into chips, concluding in the distribution of finished products to companies, retailers, and consumers across the globe. This intricate supply chain and logistics network enables the semiconductor industry to thrive despite its complexity and global competition. Each stage plays a critical role in delivering the chips that power the devices we rely on daily.
The dire need for logistics expertise
In addition to the intricate nature of semiconductor manufacturing, serving the semiconductor supply chain requires a well-honed set of logistics expertise and capabilities. These are just some of the vital components that are critical in keeping the industry’s complex global network running smoothly.
Semiconductor supply chain logistics:
- Reliable Freight Capacity: Timely and efficient transportation is crucial to meeting semiconductor production demands.
- Multi-Modal Solutions: A range of shipping options, including reliable services to cities not directly served by air freight, ensures comprehensive coverage.
- Expedited Shipping: This is essential in order to meet tight semiconductor production schedules.
- Consolidated Air Freight: Balancing speed and cost-effectiveness helps maintain efficient operations.
- Project Logistics Experience: This requires specialized expertise, particularly in managing large-scale semiconductor production.
- Bonded Warehousing: Facilities that offer this service allow for deferred duty and tax payments, optimizing financial strategies for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Customs Brokerage: This is essential for ensuring compliance with international regulations and facilitating the movement of semiconductor goods across borders.
- Secure Trucking: Specialized services for high-value semiconductor shipments, including optional escort services, enhance security during transit.
- Cross-Border Trucking: Provides a balanced approach between speed and cost-efficiency for semiconductor logistics.
By mastering these logistics expertise and capabilities, service providers can effectively support the semiconductor supply chain’s demanding requirements, ensuring the smooth flow of materials and components across the globe.
To ensure the flawless operation of this multifaceted system, top-tier logistics expertise is essential. The movement of materials and state-of-the-art technologies on a worldwide scale demands a meticulously organized logistics network to guarantee efficient and reliable deliveries.
Within this intricate network, Taiwan stands as a hub, providing the necessary expertise and resources required to strengthen the semiconductor supply chain. Taiwan’s proficiency in seamlessly connecting manufacturers, suppliers, and customers is crucial to the industry’s long-standing success.
Taiwan’s role in high-tech supply chains
Taiwan holds a strategic position within high-tech supply chains, especially in semiconductor distribution. It actively collaborates with like-minded nations to ensure smooth operations.
The semiconductor industry forms partnerships with international tech giants like Apple, Google, and Nvidia, providing them with top-tier chips for advanced devices, including high-performance computing and artificial intelligence applications.
Taiwan’s strategic location, advanced infrastructure and logistics expertise make it essential for the global technology industry.
Bonded Warehousing and Free Trade Zone Services
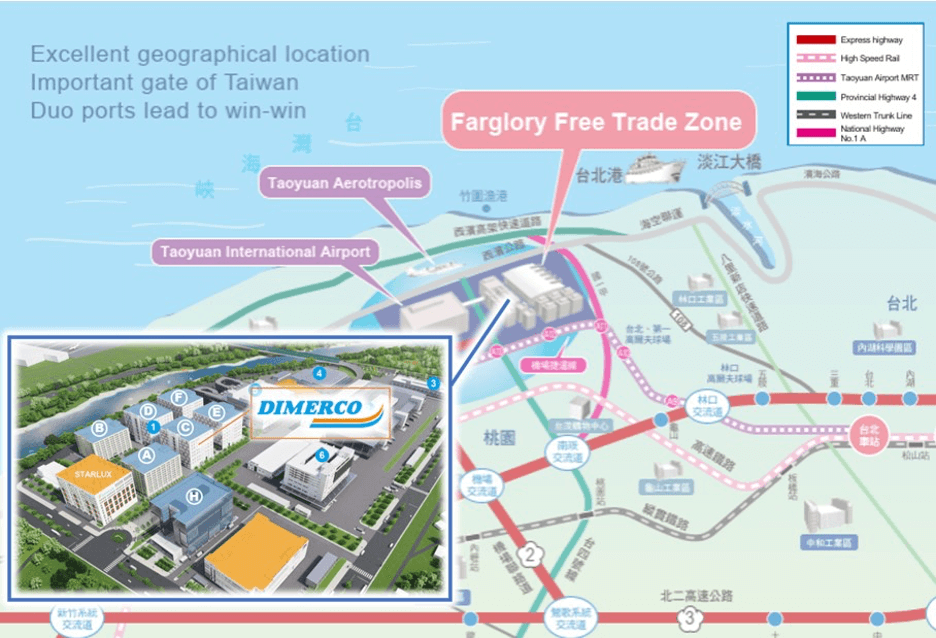
One clear example of this is Dimerco’s new bonded warehouse designed to meet the needs of high-tech supply chains operating in Taiwan. It offers a comprehensive one-stop logistics solution, covering air and ocean freight, bonded warehousing, and trade compliance services.
This is Dimerco’s second bonded warehouse, strategically located within the Taiwan Taoyuan International Airport Free Trade Zone (FTZ), ensuring faster and more efficient distribution. FTZs offer multiple benefits to businesses, and Taiwan is a significant supplier, not only to leading U.S. technology firms like Apple, Texas Instruments, and Qualcomm but also to U.S. allies globally.
This warehouse allows incoming supplier inventory to be stored duty and tax-free until shipment. Similarly, finished goods produced in Taiwan can remain in the bonded warehouse, free of duties and taxes, until they are sold and shipped.
This new facility highlights Taiwan’s commitment to high-tech supply chains but also reinforces its position as a critical link in the semiconductor supply chain, facilitating goods movement within the global tech industry.
Services for foreign companies
For foreign companies that want to do business in Taiwan without having a legal entity there, Dimerco can act as a business agent for them by applying for a “Business Agent Application” to the Taiwan National Taxation Bureau. This can apply to becoming an Importer of Record (IOR) or an Exporter of Record (EOR) on the company’s behalf.
Another advantage of a Taiwan FTZ is that corporate income tax can be exempted for certain business models if approved by CAA. Only a few 3PLs in Taiwan have the capability and experience to offer customers both business agent services and Corporate Income Tax Exemption Certificate Application services. In 2022, eight entities received the Tax Exemption Certificate issued by CAA at Taiwan Taoyuan International Airport Free Trade Zone (FTZ). Five of them are Dimerco clients.
As a high-tech manufacturing center, Taiwan can serve as a very efficient hub for outbound global distribution, connecting efficiently with all global customers. Utilizing an FTZ, manufacturers can store goods duty free until they are shipped out from the warehouse to other global markets. By partnering with a full-service 3PL like Dimerco in Taiwan, companies can access air, ocean, FTZ bonded warehousing and trade compliance services in one, integrated solution.
Shipping from Taiwan to the US
Taiwan and the US share a strong global partnership, especially in semiconductors. Major Taiwan-based carriers like China Airlines and EVA Airlines offer regular flights to and from the United States. Timely transportation is crucial, and partnering with a freight forwarder with its own loading dock in the cargo terminal ensures efficient cargo handling.
Leveraging Bonded warehouses within Taiwan’s Free Trade zone helps manage tax and duty expenses, optimizing cash flow for import and export operations.Taiwan’s FTZ offers tax benefits and the flexibility for various activities, including assembly and manufacturing.
Furthermore, in the semiconductor industry, it’s not just about the tiny chips but also about the massive, highly sensitive manufacturing equipment used in the chip-making process. These projects demand meticulous planning to move such large, valuable equipment on precise schedules.
Securing semiconductors supply chains: Taiwan’s role and global resilience
Semiconductors have become integral to a wide range of industries and are fundamental to shaping our future. The recent supply chain crisis has shed a light on the intricate nature and vulnerabilities of the semiconductor industry’s globalized supply chains. Finding solutions goes beyond striving for self-sufficiency. It requires the implementation of nuanced, targeted policies that enhance supply chain resilience, particularly in supply chain logistics.
The Taiwanese government is taking proactive steps to fortify the resilience of the nation’s industrial supply chains. By capitalizing on Taiwan’s existing competitive advantages and by consolidating and elevating the status of key national industries within the global supply chain, Taiwan remains a dominant force in the global semiconductor supply chain.
Are you seeking assistance for your semiconductor shipping needs?
Founded in Taiwan in 1971, Dimerco Express Group has maintained a strong presence in its home base, building excellent carrier relationships with Taiwan and Asia-based airlines and shipping lines. These connections empower us to meet your freight capacity needs effectively. Check out this short video to learn more about Dimerco and our logistics experience in the semiconductor sector.
To address your semiconductor logistics requirements, consult with one of our semiconductor shipping specialists.
